Plasmapheresis is a medical procedure used to remove and replace plasma to treat various conditions. It involves separating plasma from the other blood components and then either discarding the plasma or treating it before returning it to the patient.
How Plasmapheresis Works
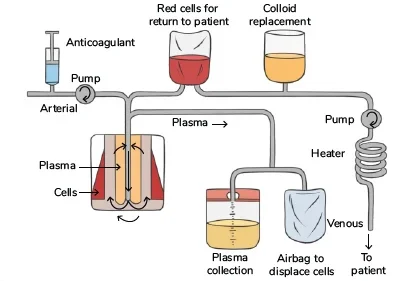
Blood is obtained from the patient’s body through a needle inserted into a vein, typically in the arm.
The blood is then processed through a machine called apheresis or a plasma separator. This machine separates the plasma from the other blood components: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
The separated plasma can be treated to remove harmful substances (e.g., antibodies and toxins) or, in some cases, discarded.
The removed plasma is replaced with a substitute fluid, such as saline, albumin, or donor plasma, which is then infused back into the patient’s bloodstream.
The treated or replacement fluid, along with the remaining blood components, is returned to the patient.
